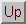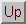


Let the parent be:
The mutation operator is defined so as to contribute to the exploratory behavior of the population of profiles. An offspring resulting from mutation searches a newer domain not covered by the parent or other members of the population. This helps the population of profiles to adapt to changing user interests. It also introduces a serendipitious element to the profiles.
The offspring is slightly different from the parent, so that the offspring explores a newer domain. At the same time, the offspring retains some attributes of the parent so that it can exploit the knowledge of the parent. This effect is achieved by modifying the newsgroup field of the profile, since this field controls the search domain of the profile. One of the newsgroups is randomly selected for replacement. This newsgroup is replaced by a randomly selected ``similar'' newsgroup.
A similarity function is defined over the set of all newsgroups, as
explained in the following paragraph. This similarity function is used
to compute a priori similarities between all pairs of
newsgroups. When the original newsgroup needs to be replaced, its
nearest neighbors are the candidates for replacement. A pre-decided
threshold, say , is used to choose the number of candidates to be
considered. Since the mutated offspring must be different from the
parent, none of the candidate newsgroups should be already present in
the parent. Once the set of
nearest neighbors not already present
in the parent is found, one of the candidate newsgroups is selected at
random. This is used as the replacement in the offspring.
To calculate the similarity between two newsgroups, both are first represented
as a vector of terms. The document frequencies of terms in a newsgroup are used
as the term weights. The document frequency for a term
in newsgroup
is
the fraction of the total number of documents in
which contain the term
.
It is calculated as shown in equation
 .
This gives a vector of terms weighted by document frequency. A similar vector
of terms is calculated for the other newsgroup
.
This gives a vector of terms weighted by document frequency. A similar vector
of terms is calculated for the other newsgroup .
The similarity between the two newsgroups is given by the cosine product of
the two vectors, as shown in equation
 .
.
where is the document frequency of term
in
newsgroup
,
is the number of documents in
which
contain the term
and
is the total number of documents
in
.
gives the similarity between
newsgroups
and
.
As in the crossover operator, the fitness of the offspring is set to
the default initial weight of .